Understanding the Basics of Employment Law in the UK: A Comprehensive Guide for HR Professionals
Employment law in the UK is a cornerstone of workplace governance, ensuring that both employers and employees operate within a framework of rights and responsibilities. For HR professionals, understanding these laws is not just about compliance; it's about fostering a workplace that is fair, equitable, and legally sound.
At the heart of UK employment law is the employment contract. This document outlines the terms and conditions of employment, including job responsibilities, pay, working hours, and notice periods. It is crucial for HR to ensure that contracts are clear and reflect both the needs of the business and the legal requirements. Any ambiguity in contracts can lead to disputes, so careful drafting and regular updates in line with changing laws are essential.

Another critical area is employee rights, which are protected by various laws such as the Equality Act 2010. This Act prohibits discrimination based on characteristics like age, gender, race, religion, sexual orientation, and disability. HR must ensure that all workplace policies and practices comply with these anti-discrimination laws. This includes recruitment, promotions, training opportunities, and even the handling of grievances.
The issue of working hours and wages is governed by laws like the Working Time Regulations and the National Minimum Wage Act. HR must ensure that employees do not exceed the maximum working hours, receive appropriate rest breaks, and are paid at least the minimum wage. These regulations are designed to protect workers' health and well-being, and failure to comply can lead to significant penalties for employers.
Dismissal is another area fraught with legal complexities. Whether it’s a case of misconduct, redundancy, or poor performance, HR must follow a fair and transparent process to avoid claims of unfair dismissal. This involves providing adequate notice, conducting proper consultations, and offering employees the right to appeal. Redundancies, in particular, require careful handling to ensure that selection criteria are fair and non-discriminatory.
Moreover, HR professionals must be aware of the legal obligations regarding workplace health and safety, which are covered by the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974. This Act requires employers to provide a safe working environment, conduct risk assessments, and take appropriate measures to prevent accidents and injuries. HR plays a crucial role in ensuring that health and safety policies are implemented and that employees are trained on safety procedures.
In summary, mastering the basics of UK employment law is essential for HR professionals to create a compliant and supportive workplace. By understanding the key legal principles, HR can not only protect the organization from legal risks but also contribute to a positive work environment where employees feel valued and secure.
The Role of HR in Navigating Post-Brexit Employment Challenges
The UK's departure from the European Union has brought about significant changes in the employment landscape, presenting new challenges and opportunities for HR professionals. The end of free movement between the UK and EU countries has particularly impacted the ability of businesses to recruit and retain talent from across Europe.
One of the most immediate challenges for HR is navigating the new immigration rules. With the introduction of the UK's points-based immigration system, HR teams must ensure that they are fully compliant with the new visa requirements. This involves verifying the right to work for all employees, managing visa applications, and staying informed about changes in immigration policy. For businesses that rely heavily on EU workers, this shift has required significant adjustments in recruitment strategies.

Another area of concern is the potential impact on employee rights. While the UK government has stated its intention to maintain high standards of workers' rights post-Brexit, there is uncertainty about how these rights will evolve over time. HR professionals need to stay vigilant and keep abreast of any changes in legislation that could affect employees' terms and conditions. This includes areas such as working hours, holiday entitlements, and protections against unfair dismissal.
Brexit has also prompted many organizations to review their employment contracts, especially those with cross-border operations. HR teams must ensure that contracts are up to date and reflect the current legal environment. This may involve revising clauses related to jurisdiction, applicable law, and the resolution of disputes. For multinational companies, it is essential to harmonize employment practices across different jurisdictions while complying with local laws.
Moreover, the uncertainty surrounding Brexit has led to concerns among employees, particularly those from EU countries, about their job security and future in the UK. HR plays a crucial role in addressing these concerns through clear communication and support. This could involve providing information about the Settled Status Scheme, offering legal advice, or simply being available to answer questions and provide reassurance.
On a broader level, Brexit has highlighted the importance of workforce planning and agility. HR professionals must now think strategically about how to attract and retain talent in a more restrictive environment. This might involve developing new talent pipelines, investing in skills development, or exploring alternative ways of working, such as remote or flexible working arrangements.
In conclusion, HR professionals are at the forefront of navigating the post-Brexit employment landscape. By staying informed, adapting to new regulations, and providing strong support to employees, HR can help organizations manage the challenges of Brexit while also seizing new opportunities in a changing job market.
The Evolving UK Job Market: Trends HR Needs to Watch in 2024
The UK job market is undergoing significant changes, driven by technological advancements, economic shifts, and evolving worker expectations. As we move into 2024, HR professionals must stay ahead of these trends to ensure that their organizations remain competitive and attractive to top talent.
One of the most prominent trends is the rise of remote and hybrid work models. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift towards remote working, and many businesses have since embraced this new way of working as a permanent option. In 2024, employees are increasingly expecting flexibility in where and how they work. HR teams need to adapt their policies to support remote work, which includes managing remote teams, ensuring productivity, and maintaining employee engagement.

Alongside this shift, there is a growing emphasis on digital skills. The increasing integration of technology into every aspect of business means that digital literacy is now a critical requirement for most roles. HR professionals must focus on both upskilling current employees and attracting new talent with expertise in areas such as data analysis, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence. This might involve partnering with educational institutions, offering training programs, or revising recruitment strategies to prioritize digital competencies.
Another trend to watch in 2024 is the increasing importance of employee well-being. The past few years have highlighted the impact of mental health on productivity and job satisfaction, and organizations are now more focused on creating supportive work environments. HR can play a key role in this by implementing wellness programs, promoting work-life balance, and providing resources for mental health support. By prioritizing well-being, businesses can improve employee retention and attract talent who value a healthy work culture.
The job market is also seeing a shift in employee expectations around company values and corporate social responsibility (CSR). More than ever, workers want to be part of organizations that align with their personal values, particularly in areas like environmental sustainability and social justice. HR professionals should take this into account when developing employer branding strategies, ensuring that the company’s values are clearly communicated and reflected in its practices.
Furthermore, the gig economy continues to grow, with more workers opting for freelance or contract-based roles rather than traditional full-time employment. This trend presents both opportunities and challenges for HR. On one hand, it offers access to a wider talent pool; on the other, it requires new approaches to workforce management, such as flexible contracts, fair pay structures, and inclusion of gig workers in company culture.
Finally, demographic changes, including an aging workforce and increasing diversity, are shaping the job market. HR professionals need to develop strategies for managing a multi-generational workforce and fostering an inclusive environment that values diversity in all its forms. This could involve offering flexible retirement plans, providing training on unconscious bias, and ensuring that recruitment processes are inclusive.
In conclusion, the UK job market in 2024 is marked by rapid change and evolving trends. HR professionals must be proactive in adapting to these trends, focusing on flexibility, digital skills, well-being, and inclusivity to attract and retain top talent in a competitive landscape.
How to Handle Redundancies in the UK: Best Practices for HR
Handling redundancies is one of the most challenging tasks for HR professionals, requiring a delicate balance between legal compliance and compassion. In the UK, redundancies must be conducted according to strict legal guidelines to avoid claims of unfair dismissal. This includes providing adequate notice, conducting consultations, and ensuring that the selection criteria are fair and non-discriminatory.
The first step in managing redundancies is clear communication. HR must ensure that employees understand the reasons behind the redundancy process and how it will affect them. This involves providing written notifications, explaining the selection criteria, and holding individual meetings with affected employees. Transparency throughout the process is crucial to maintaining trust and reducing anxiety among staff.
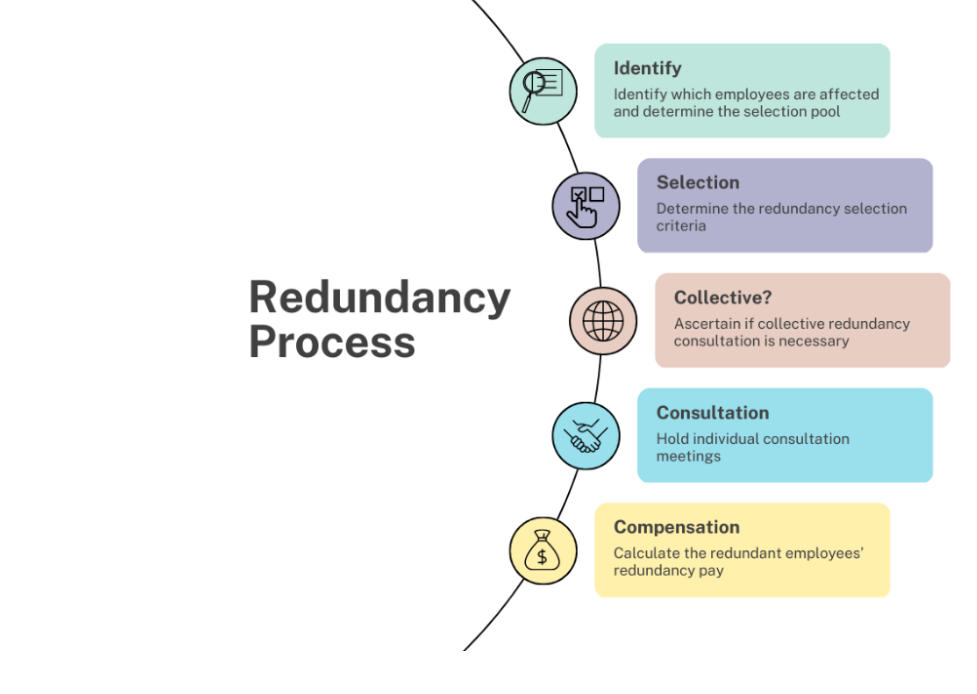
Consultation is a key legal requirement in the redundancy process. For larger-scale redundancies, employers must consult with employee representatives or trade unions. This consultation period allows employees to provide feedback and suggests alternatives to redundancy. HR should use this period to explore all possible options, such as redeployment or job-sharing, to minimize the impact on employees.
Selection criteria must be fair and objective. HR should use a transparent and consistent approach when selecting employees for redundancy, based on factors such as skills, experience, and performance. It is essential to avoid any discriminatory practices and ensure that all employees are evaluated on a level playing field.
In addition to legal compliance, HR professionals should provide practical support to employees facing redundancy. This includes offering assistance with job searching, CV writing, and interview preparation. Providing access to outplacement services can help ease the transition and support employees in finding new employment opportunities.
Post-redundancy, HR must focus on supporting the remaining employees. Redundancies can impact morale and productivity, so it is crucial to communicate the company's vision and plans for the future. This might involve organizing team-building activities, offering training programs, or holding regular check-ins to address any concerns and rebuild trust.
In summary, managing redundancies in the UK requires careful planning, clear communication, and adherence to legal requirements. By following best practices and providing support to both departing and remaining employees, HR professionals can navigate the redundancy process with sensitivity and fairness.
Promoting Diversity and Inclusion in the UK Workplace: Legal and Practical Considerations
Promoting diversity and inclusion (D&I) in the workplace is not just a legal obligation but a strategic advantage for organizations in the UK. The Equality Act 2010 provides a framework for preventing discrimination and ensuring equal opportunities for all employees. For HR professionals, creating a diverse and inclusive workplace involves both understanding legal requirements and implementing practical measures to support an inclusive culture.
One of the first steps in promoting D&I is ensuring that recruitment practices are free from bias. This includes using inclusive language in job descriptions, employing diverse interview panels, and actively seeking candidates from underrepresented groups. Training for hiring managers on unconscious bias can also help ensure that recruitment decisions are made fairly and objectively.

Creating an inclusive culture goes beyond recruitment. HR should implement policies and practices that support diversity throughout the employee lifecycle. This might include setting up employee resource groups, offering mentorship programs, and ensuring equal access to career development opportunities. An inclusive culture also requires proactive measures to address discrimination and harassment, with clear procedures for reporting and resolving issues.
Legal compliance is a critical aspect of promoting D&I. The Equality Act 2010 mandates that employers make reasonable adjustments for employees with disabilities, ensure equal pay for equal work, and prevent discrimination in the workplace. HR must stay informed about these legal requirements and ensure that the organization’s policies and practices are compliant. Regular training on D&I issues for both HR staff and employees can help maintain compliance and foster an inclusive environment.
Beyond legal requirements, there are numerous benefits to promoting diversity and inclusion. Research shows that diverse teams are more innovative, make better decisions, and have higher levels of employee engagement. By fostering a diverse and inclusive workplace, organizations can attract and retain top talent, improve employee satisfaction, and enhance their market reputation.
Moreover, companies that prioritize D&I are more likely to appeal to customers and clients who value these principles. This can lead to increased business opportunities and a competitive edge in the market. HR can play a key role in aligning D&I strategies with the organization’s business goals and measuring progress through regular surveys and audits.
In conclusion, promoting diversity and inclusion in the UK workplace is both a legal requirement and a business imperative. HR professionals have a vital role in creating an inclusive culture that values diversity and supports all employees, contributing to a more successful and innovative organization.
Navigating the Complexities of TUPE Transfers in the UK: A Guide for HR
The Transfer of Undertakings (Protection of Employment) Regulations 2006, commonly known as TUPE, is a key piece of employment legislation in the UK. TUPE protects employees’ rights when the business they work for is transferred to a new owner, such as in the case of mergers, acquisitions, or outsourcing. For HR professionals, understanding and managing TUPE transfers is essential to ensure legal compliance and a smooth transition.
Under TUPE, employees automatically transfer to the new employer on the same terms and conditions as their existing contracts. This means that their continuity of employment is preserved, and they retain all their rights, including pay, holiday entitlement, and any accrued benefits. HR professionals must ensure that the transfer process is handled properly and that employees are fully informed about the implications for their employment.

A critical aspect of managing a TUPE transfer is the consultation process. Employers are required to inform and consult with affected employees or their representatives before the transfer takes place. This consultation period is an opportunity to address any concerns employees may have and to discuss potential alternatives to redundancy. HR should prepare to answer questions about job security, changes in terms and conditions, and any other issues that arise during this period.
Handling employee liabilities is another important consideration. The new employer inherits all existing liabilities related to the transferring employees, including ongoing disciplinary actions, disputes, or unpaid wages. HR must work with legal and financial teams to identify and manage these liabilities effectively, ensuring that all issues are addressed before the transfer is completed.
Post-transfer, HR professionals need to focus on integrating the transferred employees into the new organization. This includes providing induction programs, facilitating training, and ensuring open communication channels to address any concerns. It is also important to support existing employees and promote a positive working environment to foster teamwork and collaboration between new and existing staff.
Changes to terms and conditions post-transfer must be approached with caution. While TUPE protects employees’ existing terms at the point of transfer, any changes made afterward must be agreed upon with employees and cannot be solely for economic, technical, or organizational reasons. HR should handle any harmonization of terms and conditions carefully to avoid potential legal challenges.
In conclusion, managing TUPE transfers requires careful planning, clear communication, and a thorough understanding of the legal framework. By following best practices and providing strong support to employees throughout the transfer process, HR professionals can ensure a smooth transition and maintain employee trust and morale.
The Impact of the UK’s National Living Wage on Employment: An HR Perspective
The introduction and ongoing adjustments to the UK’s National Living Wage (NLW) have had a significant impact on the employment landscape. Since its implementation in 2016, the NLW has set a minimum hourly rate that employers must pay to workers aged 23 and over. As of April 2024, the NLW stands at £11.68 per hour, reflecting the government's commitment to ensuring fair pay and reducing in-work poverty.
For HR professionals, the NLW presents both opportunities and challenges. On the positive side, paying the NLW helps to attract and retain employees by offering a fair wage. This can lead to increased employee satisfaction and lower turnover rates, which are beneficial for business stability. However, the increase in wage costs can also pose challenges, particularly for small businesses or those with tight profit margins.

One of the key challenges for HR is managing the impact of the NLW on the overall wage structure within the organization. As the NLW increases, it can lead to wage compression, where the pay gap between lower-paid and higher-paid employees narrows. This can cause dissatisfaction among more experienced or skilled workers who may feel their pay does not adequately reflect their experience or contribution. HR needs to address this issue by reviewing and adjusting the entire wage structure to maintain appropriate pay differentials.
Compliance with the NLW is also critical. HR must ensure that all employees are paid at least the NLW, monitor pay rates, and make necessary adjustments when the NLW increases. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties and damage to the organization’s reputation. Regular audits and updates to payroll systems can help maintain compliance and avoid potential issues.
Beyond compliance, HR professionals can proactively manage the financial impact of the NLW by exploring ways to improve productivity. This might involve investing in employee training, optimizing work processes, or implementing new technologies to enhance efficiency. By improving productivity, businesses can offset some of the increased wage costs and maintain profitability.
Additionally, HR should consider the broader implications of the NLW on employee relations and morale. While the NLW is generally viewed positively, it can also create tensions if employees feel the increase is insufficient to meet their living costs. HR can address these concerns by offering additional support, such as financial wellness programs or assistance with budgeting.
In conclusion, the UK’s National Living Wage has a significant impact on employment practices and HR strategies. By ensuring compliance, managing wage structures effectively, and addressing employee concerns, HR professionals can navigate the challenges of the NLW while leveraging its benefits to enhance employee satisfaction and organizational performance.
Effective Strategies for Employee Engagement and Retention in the UK
Employee engagement and retention are crucial for the success of any organization. Engaged employees are more productive, motivated, and committed to their work, which directly impacts organizational performance. For HR professionals, developing effective strategies to enhance engagement and reduce turnover is a key responsibility.
One effective strategy is to foster a positive work environment. This includes creating a culture of recognition and appreciation where employees feel valued for their contributions. Regular feedback, both formal and informal, and recognition programs can boost morale and encourage employees to stay committed to the organization. Additionally, promoting a healthy work-life balance through flexible working arrangements and wellness programs can enhance job satisfaction.

Career development opportunities are another important factor in employee retention. Employees are more likely to stay with an organization that invests in their growth and development. HR professionals should offer training programs, mentorship opportunities, and clear career progression paths to help employees achieve their professional goals. Providing support for further education and skill development can also demonstrate a commitment to employees’ long-term success.
Employee engagement surveys are a valuable tool for understanding the needs and concerns of the workforce. Regular surveys can provide insights into factors that affect engagement and help identify areas for improvement. HR can use this feedback to make informed decisions and implement changes that address employee concerns and enhance overall job satisfaction.
Another key strategy is to ensure effective communication within the organization. Transparent communication about company goals, changes, and expectations helps build trust and keeps employees informed. HR should facilitate open channels of communication, such as regular team meetings and one-on-one check-ins, to ensure that employees feel heard and valued.
Compensation and benefits also play a significant role in employee retention. Offering competitive salaries and comprehensive benefits packages can help attract and retain top talent. HR professionals should regularly review and benchmark compensation packages to ensure they remain competitive and aligned with industry standards.
Finally, fostering a strong organizational culture that aligns with employees’ values and expectations can greatly enhance engagement and retention. HR should work to create a culture that reflects the organization’s mission and values, supports diversity and inclusion, and promotes a positive and inclusive work environment.
In conclusion, effective strategies for employee engagement and retention involve creating a supportive work environment, offering career development opportunities, utilizing engagement surveys, ensuring transparent communication, providing competitive compensation, and fostering a strong organizational culture. By implementing these strategies, HR professionals can enhance employee satisfaction, reduce turnover, and contribute to the long-term success of the organization.
